No products in the cart.
Erectile Dysfunction
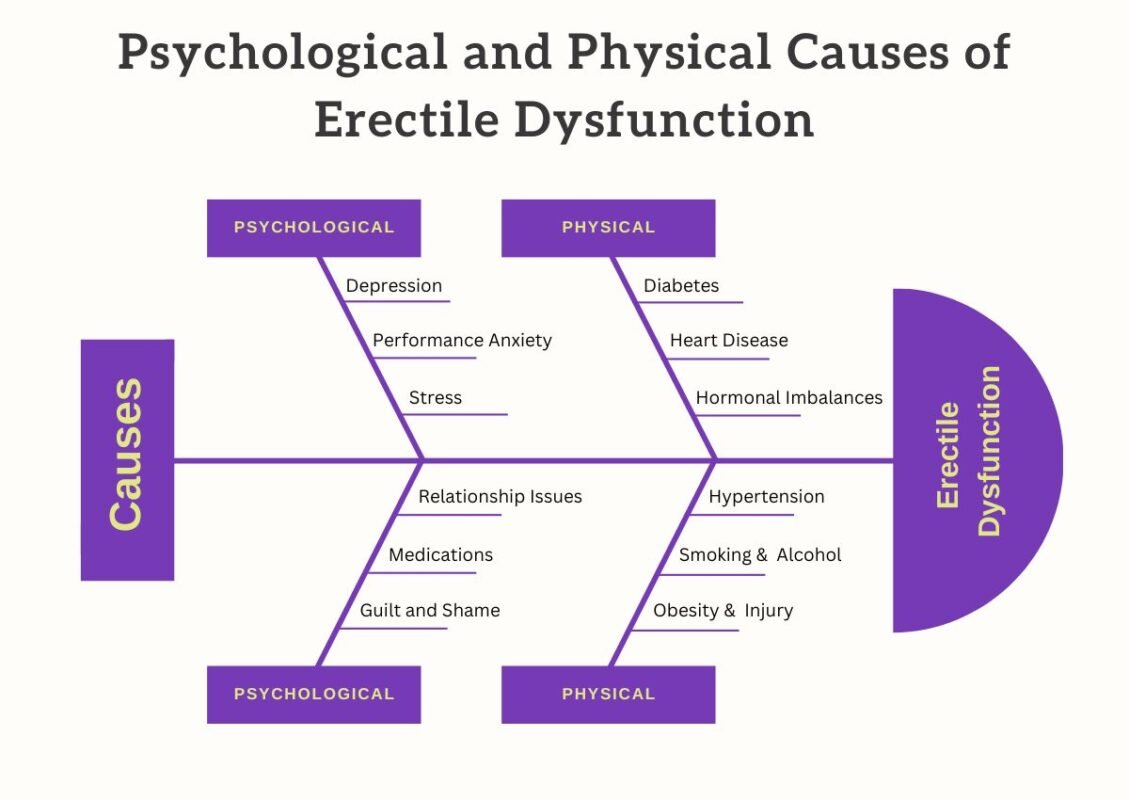
Psychological and Physical Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction can be a complex issue affecting many men. This article aims to shed light on the various factors that can contribute to erectile dysfunction. We’ll delve into both the psychological and physical aspects that can impact a man’s ability to achieve or maintain an erection. Understanding these causes is the first step towards addressing the issue and exploring potential solutions.
Table of Contents
Psychological Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
The mind plays a significant role in sexual function. Psychological factors can contribute to erectile dysfunction. These mental and emotional factors can sometimes be the root cause or can worsen physical conditions that lead to ED. It’s important to understand that your mental health can directly impact your sexual health.
Performance Anxiety
Performance anxiety is a common psychological cause of ED. Feeling stressed about sexual performance can create a cycle where the anxiety itself interferes with the ability to achieve or maintain an erection. This fear of failure can be overwhelming and contribute to ED.
Depression
Depression, a mood disorder characterized by persistent sadness and loss of interest, can significantly impact sexual desire and function. Men with depression often experience changes in libido, difficulty achieving or maintaining erections, and reduced sexual satisfaction.
Relationship Issues
Relationship problems can create emotional stress that negatively affects sexual intimacy. Conflicts, lack of communication, and dissatisfaction with the relationship can contribute to ED. These issues can lead to anxiety, decreased self-esteem, and a lack of desire, impacting erectile function.
Stress
Stress is a common culprit behind erectile dysfunction. When you’re constantly stressed, your body’s resources are diverted to managing that stress, leaving less energy for sexual arousal. Chronic stress can also lead to hormonal imbalances that affect sexual desire and function.
Body Image and Self-Esteem
How you feel about your body can significantly influence your sexual confidence. Negative body image can lead to self-doubt and anxiety, making it difficult to relax and enjoy intimacy. These emotional factors can contribute to erectile difficulties.
Guilt and Shame
Guilt and shame about past sexual experiences can significantly impact sexual function. Negative emotions associated with these experiences can create anxiety and hinder sexual arousal. It’s essential to remember that everyone has a sexual history, and it’s okay to seek support if these feelings are affecting your life.
Medications
Certain medications used to treat mental health conditions like anxiety and depression can contribute to erectile dysfunction. These drugs can interfere with the body’s natural ability to achieve and maintain an erection. If you’re concerned about this, it’s important to discuss your options with a healthcare provider.
Physical Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is often connected to underlying physical health issues. Several chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease, can contribute to ED by affecting blood flow, nerve function, or hormone levels. Additionally, conditions like Parkinson’s disease can impact sexual performance. Let’s delve deeper into how these physical factors can influence erectile function.
Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases can significantly impact your overall health, including your sexual function. Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and Parkinson’s disease can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Diabetes
Diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels, which are crucial for achieving and maintaining an erection. Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can increase your risk of ED.
Hypertension
High blood pressure puts strain on your cardiovascular system, including the blood vessels that supply blood to the penis. This can hinder blood flow and contribute to erectile difficulties.
Heart Disease
Heart disease often involves blockages in the arteries, which can reduce blood flow to the heart and penis. ED can be an early warning sign of underlying heart problems.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological condition that can affect various bodily functions. It’s characterized by tremors, stiffness, and slow movement. While primarily associated with motor symptoms, Parkinson’s can also impact a person’s emotional and sexual well-being.
Vascular Issues
Vascular problems can significantly impact a man’s ability to achieve and maintain an erection. These issues relate to the blood flow necessary for a healthy erection.
- Atherosclerosis: This condition involves the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can narrow them and reduce blood flow. When this happens in the arteries leading to the penis, it can interfere with the erection process.
- High cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can contribute to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of reduced blood flow to the penis.
- Peyronie’s disease: This condition causes scar tissue to form in the penis, leading to pain, curvature, and potential erectile dysfunction.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of vascular issues that can contribute to ED. If you’re concerned about erectile dysfunction, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a crucial role in many bodily functions, including sexual arousal. Testosterone, often called the “male hormone,” is particularly important for maintaining healthy erectile function
Hypogonadism is a condition where the body doesn’t produce enough testosterone. This hormonal imbalance can lead to various symptoms, including erectile dysfunction. It’s essential to note that low testosterone isn’t the only cause of ED, and other factors often contribute to this condition.
Lifestyle Factors and ED
Your lifestyle plays a significant role in your overall health, including your sexual well-being. Certain habits can negatively impact erectile function. Let’s explore some common lifestyle factors linked to ED.
Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for ED. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the penis. This can make it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can impair erectile function. Alcohol affects the nervous system and interferes with the body’s ability to achieve an erection.
Obesity
Obesity is linked to several health issues, including ED. Excess weight can contribute to hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and heart disease, all of which can negatively impact erectile function.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Regular physical activity is essential for overall health, including sexual health. Exercise helps improve blood circulation, heart health, and hormone levels, all of which are important for erectile function.
Injury
Pelvic or spinal injuries can sometimes lead to ED. These injuries might damage nerves or blood vessels crucial for erections. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment if you’ve experienced such an injury and are experiencing ED.
Prostate Issues
Prostate problems can sometimes lead to erectile dysfunction. Two common prostate conditions linked to ED are prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Prostate cancer is a serious condition where abnormal cells grow in the prostate gland. While treatments for prostate cancer can often lead to ED, it’s essential to remember that ED can also occur before, during, or after treatment.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate. As the prostate grows, it can put pressure on the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. This pressure can sometimes affect erectile function.
It’s important to note that not all men with prostate problems will experience ED. The severity of ED can vary depending on the individual and the specific prostate condition.
Common Myths About Erectile Dysfunction
There are many misconceptions about erectile dysfunction. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones.
Accutane causes ED.
Accutane is a medication often used to treat severe acne. While it can have side effects, ED is not typically listed among them. However, some studies suggest a possible link between Accutane and ED. It’s essential to remember that individual reactions to medications can vary, and if you’re concerned about the potential side effects of Accutane, it’s crucial to discuss this with your healthcare provider.
Melatonin supplements cause ED.
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the body that regulates sleep. While it’s available as a supplement, there’s no concrete evidence linking melatonin to ED. However, some people have raised concerns about this potential connection. If you’re wondering whether melatonin causes ED, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health situation.
Tight clothes cause ED.
While extremely tight clothing can restrict blood flow to certain areas, including the genitals, there’s no direct evidence linking it to ED. However, wearing uncomfortable or restrictive clothing can generally impact overall comfort and well-being, which might indirectly affect sexual performance. Choosing comfortable attire is always advisable. If you’re concerned about the potential impact of tight underwear on erectile function, you might want to check out our article on tight underwear cause ed for more information.
Conclusion
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. As we’ve explored, both psychological and physical causes of erectile dysfunction. From performance anxiety and relationship issues to chronic diseases and lifestyle choices, the causes of ED are diverse. It’s essential to recognize that ED is often a complex interplay of these factors. If you’re experiencing ED, understanding the potential underlying causes can be the first step toward finding appropriate solutions.
Reference
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/-/media/Files/Urologic-Diseases/Erectile_Dysfunction_Section_508.pdf
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/252252265/252252265